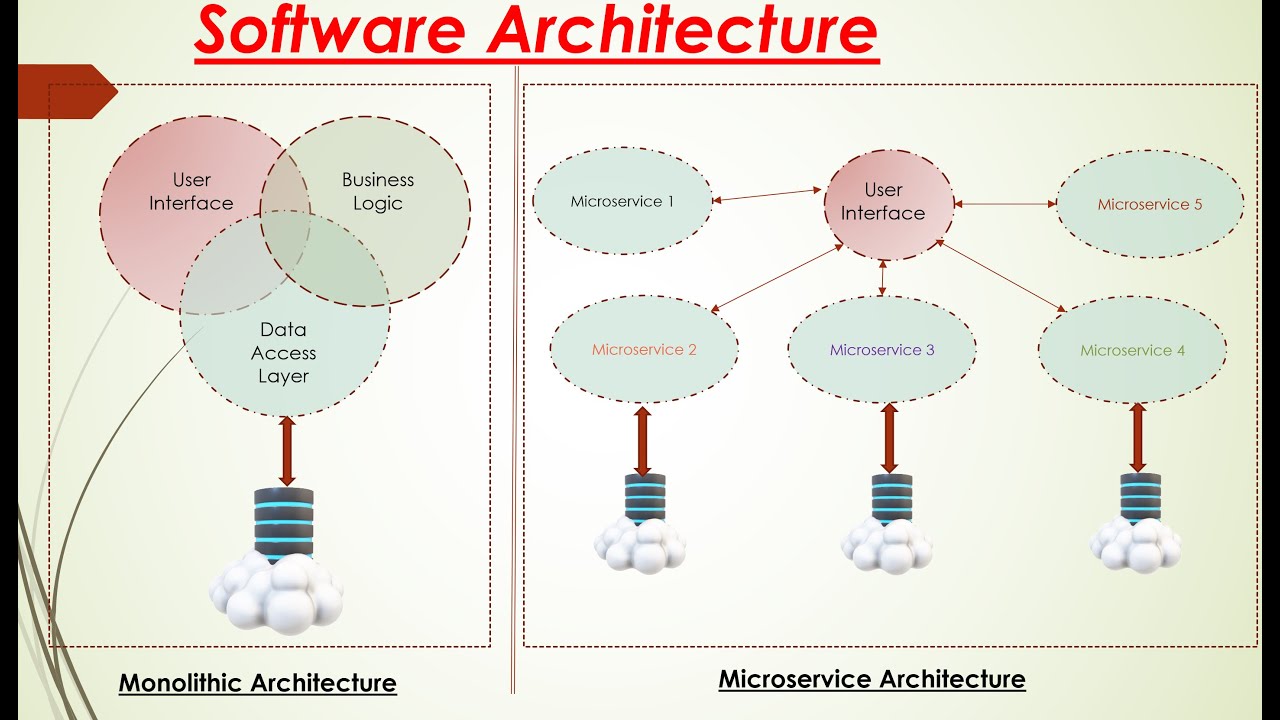
Modern software architecture has shifted significantly over the past decade. One of the most influential changes is the adoption of microservices architecture, where applications are built as a collection of small, independent services rather than a single monolithic system. This approach improves flexibility, scalability, and resilience.
Each microservice is responsible for a specific function and can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently. This allows development teams to work in parallel and release updates more frequently. As a result, organizations can respond faster to user feedback and market demands without disrupting the entire system.
Microservices also improve system reliability. If one service fails, others can continue to operate, reducing the risk of total system downtime. This is especially important for large platforms that must remain available around the clock. Containerization and orchestration tools further simplify the management of microservices environments.
However, microservices introduce new challenges. System complexity increases as the number of services grows. Effective monitoring, communication, and security strategies are essential to maintain stability. Clear documentation and strong DevOps practices play a key role in successful implementation.
When designed correctly, microservices architecture enables long-term scalability and innovation. It supports continuous improvement while maintaining system stability and performance.